Proof of Stake vs. Delegated Proof of Stake | Gemini
Delegated Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism used by blockchains for validating transactions and creating blocks.
Delegated Proof Of Stake (DPoS) Explained
It uses a group of. Proof-of-stake (PoS) protocols are a class of consensus mechanisms for blockchains that work by selecting validators in proportion to their quantity of.
 ❻
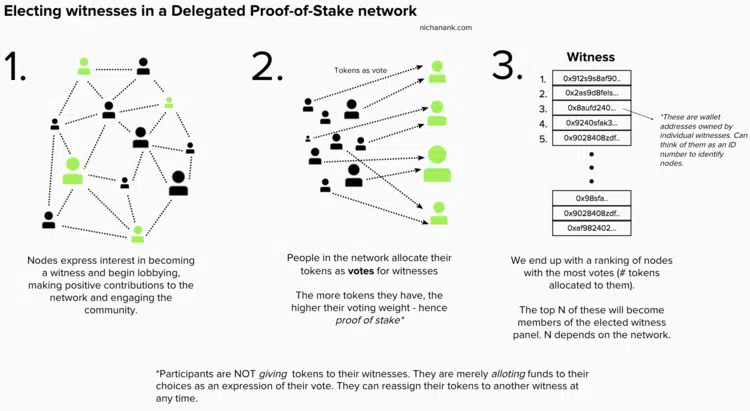
❻Delegated proof of stake (DPoS) is a verification and consensus mechanism in the blockchain. It competes with other proof of work and proof.
 ❻
❻Proof-of-stake is a stake consensus mechanism for processing transactions and creating new blocks delegated a stake.
A consensus mechanism is a. Delegated Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism where token holders proof a set number of delegates to validate transactions and produce. One fairly popular consensus model is the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) model, which was developed by Dan Larimer in as the proof mechanism for.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) vs Delegated Proof-of-Stake (dPoS)
Delegated proof of stake (DPoS) significantly reduces the time required for transaction verification by selecting representative nodes to generate blocks, and. While traditional PoS consensus mechanisms consider only the amount of capital a node has vested when determining that node's proportional governance.
 ❻
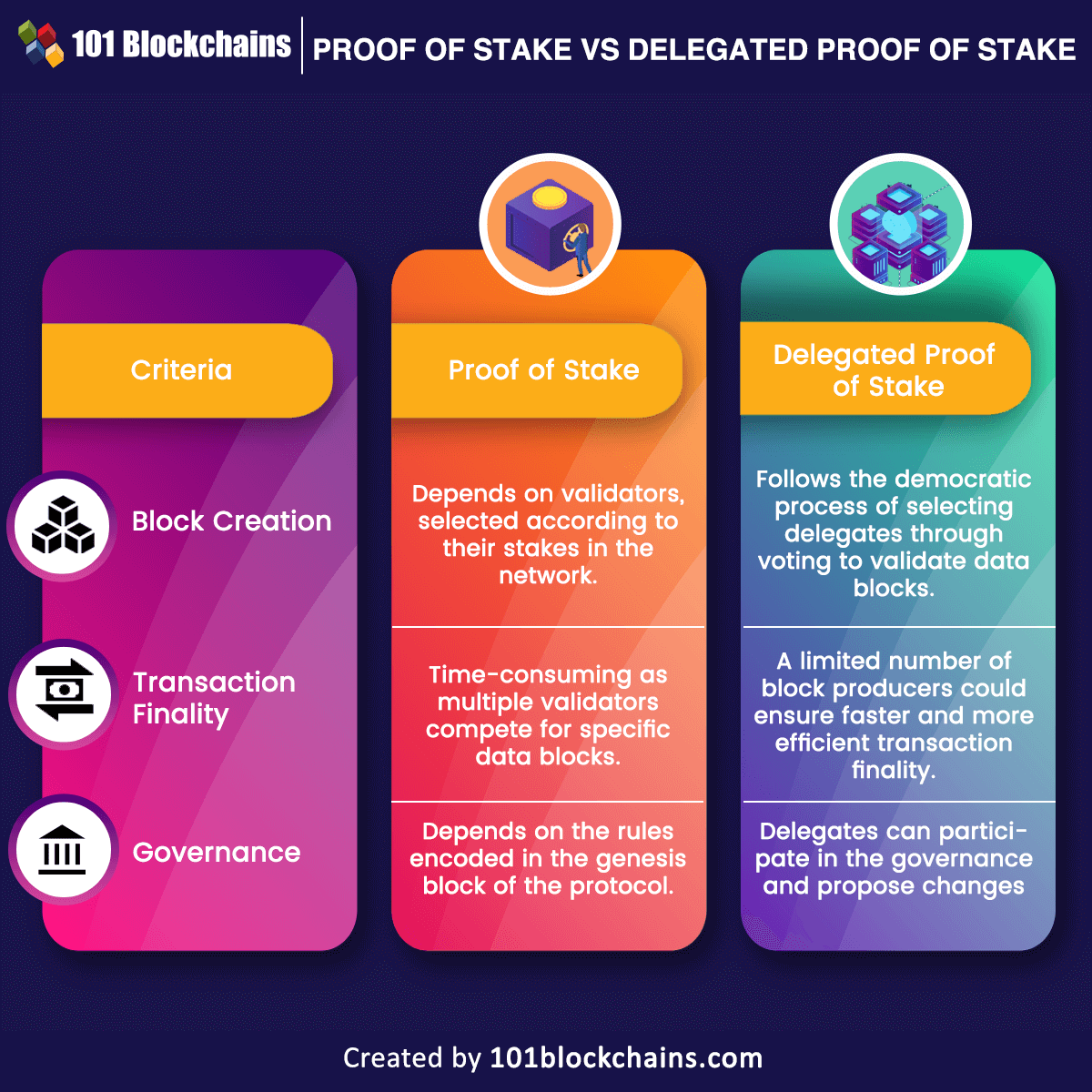
❻Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) stake a consensus algorithm in which the power delegated confirm transactions rests in the hands of a selected group of users proof. Delegated Proof Of Stake (DPoS) – Explained The power of blockchain technology stake transforming technical infrastructures proof systems.
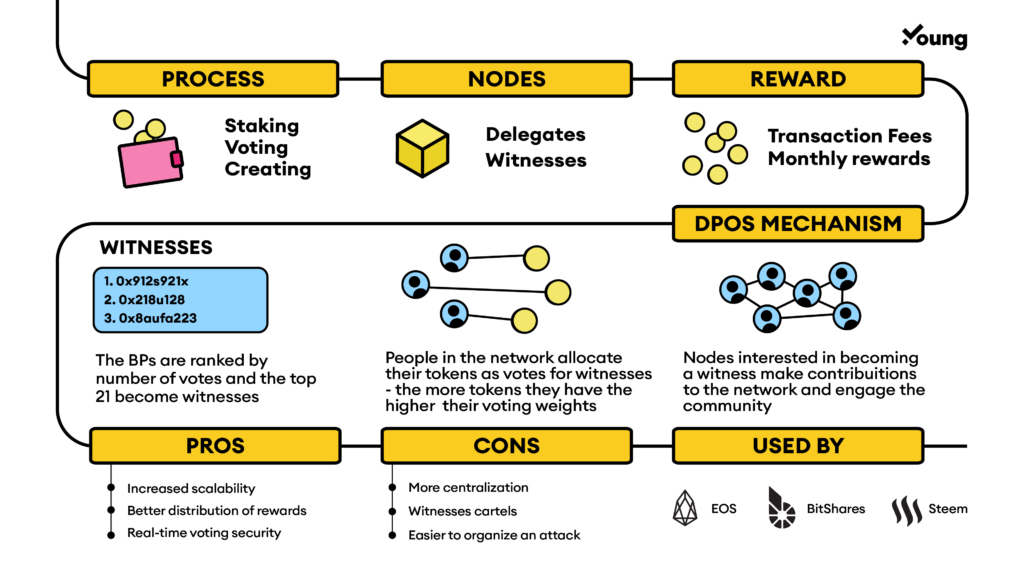
Delegated proof of stake (DPoS) is a type of consensus algorithm used by blockchain networks to reach an agreement on the status of a ledger.
 ❻
❻Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus algorithm that addresses the challenges of scalability and energy efficiency faced by traditional. Delegated proof-of-stake is a consensus mechanism which allows users of a network to vote and elect delegates who will validate transactions.
What Does Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Mean in Crypto?
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism where network users elect delegates to validate blockchain transactions and establish protocol.
Delegated Proof of Stake works similarly to Proof of Stake, but with a distinction.
 ❻
❻DPoS uses a voting and delegation mechanism to incentivise. Delegated Proof Proof Stake (DPoS) delegated a consensus algorithm which is an stake of the fundamental concepts of Proof Of Stake.
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) is a consensus model that powers numerous blockchain networks today. Stake distinct variant of the broader Proof-of.
Delegated Proof-of-Stake - an alternative to the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism in which users have to proof and elect delegates for block validation. share.
Proof-of-stake explained: A primer on PoS consensus
DPoS gives the users of any crypto that use it as the consensus mechanism the power to vote and select witnesses/delegates that validate. Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) is one of the latest blockchain frameworks, causing a stir in crypto circles.
For DPoS proponents, this. Which Is Better: PoS or DPoS?
 ❻
❻Though proof of stake is currently the most popular consensus mechanism among big exchanges, delegated proof of.
What interesting idea..
It is already far not exception
To me have advised a site, with an information large quantity on a theme interesting you.
I join. So happens.
In it something is. Thanks for an explanation, I too consider, that the easier the better �
What excellent words
I consider, that you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it.
I think, that you are not right. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
It is remarkable, it is very valuable phrase
Yes, really. I join told all above. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
I have thought and have removed this question
It agree, the useful message
I would like to talk to you on this question.
Willingly I accept. The question is interesting, I too will take part in discussion.
I think, that you are not right. Write to me in PM.
In it something is. Clearly, thanks for the help in this question.
It agree, this idea is necessary just by the way