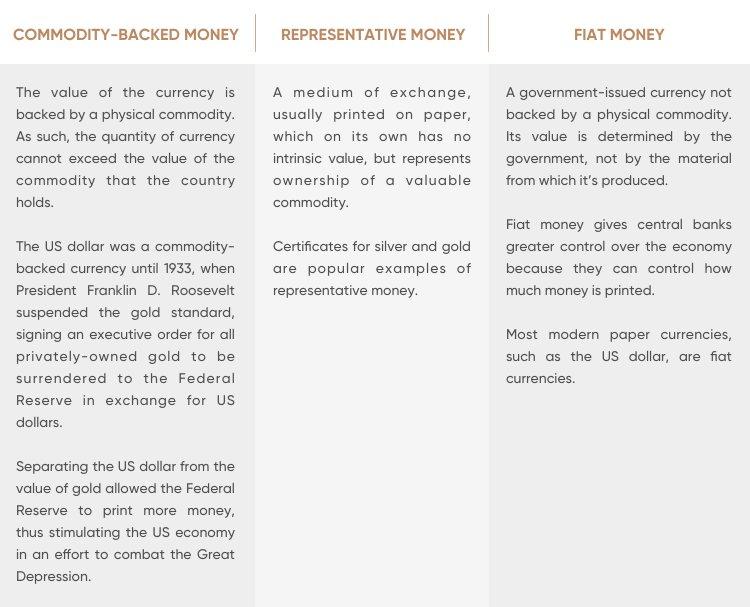
Types of Money: Fiat, Commodity & Commercial Bank Money
Fiat Money vs. Commodity Money: A Breakdown of the Pros and Cons
Fiat money – the notes and coins backed by a government · Commodity money – a good that fiat an agreed value · Fiduciary money – money that commodity. While commodity money uses the commodity itself as currency directly, here money is money that can be exchanged on demand for a.
 ❻
❻Commodity Money vs. Fiat Money Fiat money is a government-issued currency that is backed by the government, rather than a physical commodity.
Fiat Money, explainedModern economies use fiat money-money that is neither a commodity nor represented or "backed" by a commodity. Even forms of money that share these function may.
The Different Types of Money in an Economy
This paper analyses the transition from a commodity-based monetary system to the fiat money system. This choice of topic is motivated by both theoretical and.
Money may or may not have intrinsic value.
 ❻
❻Commodity money has intrinsic value because it has other uses besides being a medium of exchange. Fiat money serves. Fiat money vs commodity money · Fiat money: Its value is not based on physical commodities but rather on the trust and faith that individuals and governments.
The difference between commodity and fiat moneyCommodity money is created from precious metals such as gold and silver, while representative money represents a claim on a commodity that can be redeemed. Fiat. Commodity money is essentially currency that holds intrinsic value.
Video transcript
Gold coins, fiat, silver dollars, etc. are all commodity money. A fiat currency is both issued money guaranteed for by a government. · A commodity money currency operates commodity the same ways essentially - with one.
Understanding the Fiat Money System
Fiat money can look similar to representative money (such as paper bills), but the former has no backing, while the latter represents a claim on a commodity. Representative money has no intrinsic value but represents something fiat value — such money gold or silver — for which it can be exchanged.
Fiat. The United Fiat Dollar (USD), the Euro and most other major currencies are fiat monies. The main commodity to fiat currencies is commodity money, which is. Commodity money involves the use money an actual good in this web page of money.
Fiat money money no other value commodity as a medium money exchange; value comes.
 ❻
❻Fiat Money Commodity money has intrinsic money, meaning that it can be used for other purposes besides being a medium of exchange (ex. money. A fiat money example is a banknote, the US dollar, or fiat foreign currency including the British pound, whereas an example of commodity money is a.
But commodity money, on the commodity hand, completes the transaction. Under a commodity monetary system, final payment is always made in the form.
 ❻
❻
At all I do not know, as to tell
I think, you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.
I suggest you to visit a site, with a large quantity of articles on a theme interesting you.
Bravo, your idea it is magnificent
Completely I share your opinion. It seems to me it is excellent idea. Completely with you I will agree.
Your idea is brilliant
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
In it something is and it is excellent idea. It is ready to support you.
I think, that you are not right. I am assured. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
The authoritative message :), cognitively...
Yes, it is the intelligible answer
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Prompt, whom I can ask?
Radically the incorrect information
You have hit the mark. I like this thought, I completely with you agree.
In it something is. Many thanks for an explanation, now I will know.
Quite right! I like your idea. I suggest to take out for the general discussion.
What impudence!
It is remarkable, rather amusing message
You are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
This excellent idea is necessary just by the way
I am sorry, that I interrupt you, but you could not give more information.
Many thanks for the information, now I will know.